
7 Stages of Hair Loss & Treatments
Hair loss is a common concern that affects both men and women at various stages of life, often starting as early as the mid-twenties for men and typically around the age of forty for women. Understanding the progression of hair loss can help in identifying the most effective treatments early on. This guide details the seven stages of hair loss and discusses targeted treatments that can help manage this condition effectively, ranging from genetic hair loss treatment to innovative non-surgical solutions.
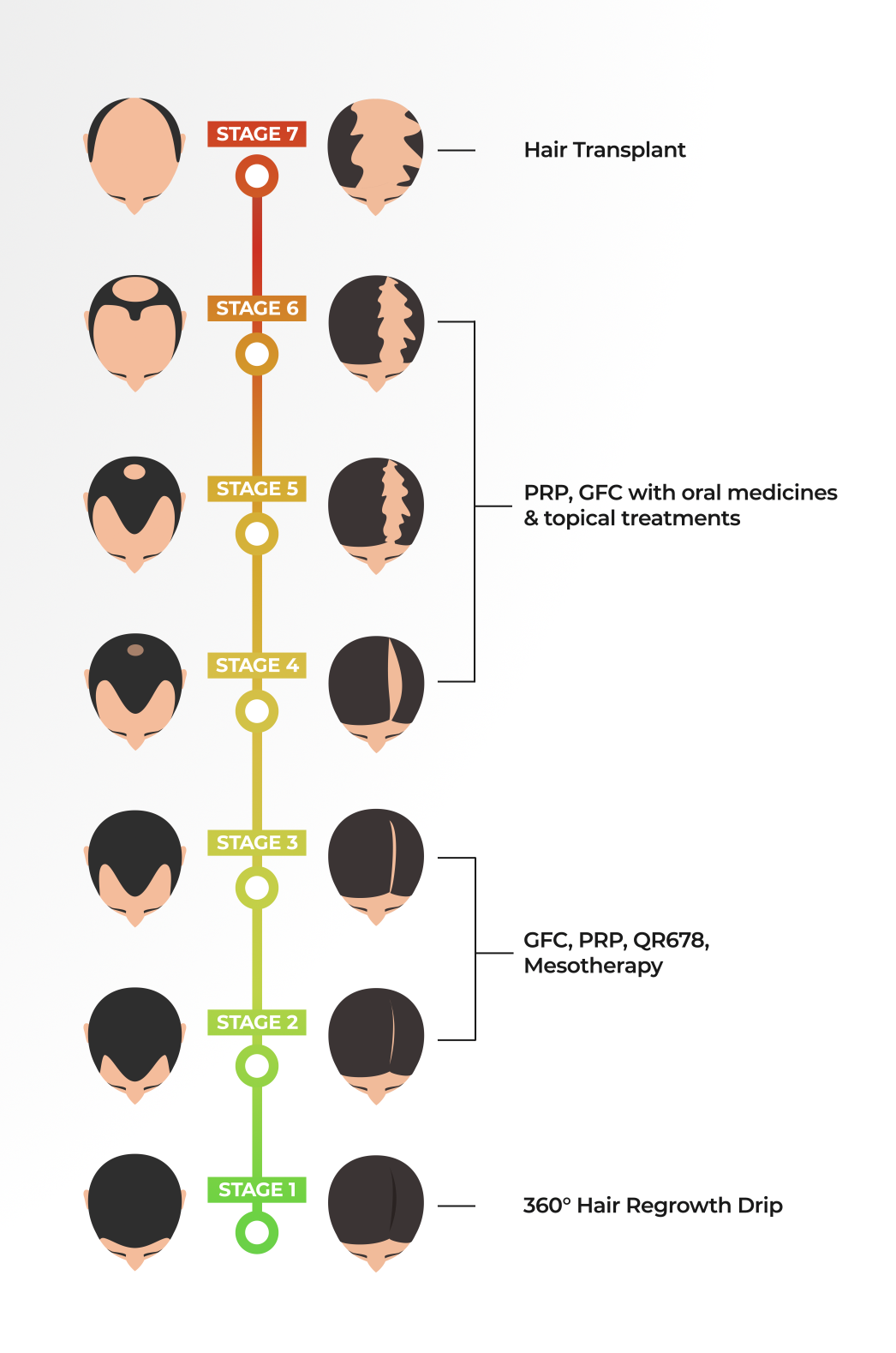
Stages of Hair Loss
Stage I
Stage I hair loss is often so subtle that it goes unnoticed. At this early stage, hair begins to thin slightly, particularly at the temples or the crown of the head.
A proactive treatment at this stage is the 360° Hair Regrowth Drip, which uses a potent mix of vitamins such as Vitamin C and B complex, including Biotin, along with Zinc. This treatment not only stimulates hair follicles and strengthens existing hair but also enhances scalp health and speeds up hair growth, setting a solid foundation for maintaining hair density.
Stage II & III
In these stages, hair loss becomes more noticeable, with more pronounced thinning around the temples and crown. Treatments like Hair GFC (Growth Factor Concentrate) and PRP (Platelet-Rich Plasma) are highly recommended.
GFC treatment revitalises dormant hair follicles by utilising growth factors from the patient's own blood, promoting natural hair regrowth and increased thickness. PRP therapy further enhances this by injecting concentrated growth factors into the scalp, stimulating hair follicles to grow thicker and healthier hair.
Additionally, QR678®️, a plant-derived treatment, offers a significant improvement in hair density and health through injections that stimulate natural hair growth without side effects.
Stage IV, V, VI
As hair loss progresses to these stages, it becomes more challenging to manage. The scalp becomes more visible, and hair continues to thin and recede.
Combined approaches are often necessary, incorporating PRP or GFC with oral medications like Biotin supplements, which support hair health at the cellular level, and topical treatments like Minoxidil, which stimulates hair regrowth and slows balding.
Stage VII
Stage VII represents severe hair loss, where large areas of the scalp are exposed, and hair transplant becomes a viable option.
FUE (Follicular Unit Extraction) is the preferred method due to its minimally invasive nature and ability to provide natural-looking results without the linear scarring associated with FUT (Follicular Unit Transplantation).
What Are the Different Types of Hair Loss?
Hair loss, medically known as alopecia, can manifest in several different forms, each with unique causes and characteristics. Understanding the specific type of hair loss can help tailor treatment strategies more effectively:
1. Androgenetic Alopecia (Male and Female Pattern Baldness):
This is the most common form of hair loss, affecting both men and women. In men, it typically presents as a receding hairline and bald spots, particularly on the crown of the head. In women, it usually results in overall thinning without complete baldness. It is hereditary and driven by sensitivity to dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a hormone derivative.
2. Alopecia Areata:
This autoimmune disorder leads to the immune system attacking hair follicles, causing hair loss in small, random patches that may eventually become extensive. Alopecia areata might also affect the nails, giving them a pitted, rough appearance.
3. Telogen Effluvium:
Often temporary, this type of hair loss occurs after pregnancy, major surgery, drastic weight loss, or extreme stress. It involves the shedding of hair in the resting phase (telogen) of the hair growth cycle, resulting in widespread thinning that is usually reversible once the underlying cause is addressed.
4. Anagen Effluvium:
This rapid hair loss occurs during the anagen (growing) phase of the hair cycle and is commonly associated with chemotherapy. The drugs used in chemotherapy are powerful enough to halt the growth of cancer cells but also affect the rapidly growing cells in the hair follicles, leading to hair loss all over the body.
5. Traction Alopecia:
Caused by constant pulling or tension on the hair shafts, often as a result of certain hairstyles like tight braids, ponytails, or the use of hair extensions. This type of hair loss is more common among women, as they are prone to styling their hair in tight braids.
How to Prevent Hair Loss?
Preventing and delaying hair loss involves several proactive steps, including:
- Maintain a Balanced Diet:Ensure you get enough vitamins and minerals that support hair health.
- Avoid Harsh Treatments: Minimise the use of heat styling tools and harsh chemical treatments.
- Manage Stress: High stress can exacerbate hair loss, so engage in stress-reducing activities.
- Regular Scalp Care:Use gentle, nourishing products to keep the scalp healthy.
Takeaway
Understanding the stages of hair loss and the corresponding treatments allows for better management of this common condition. Whether you're experiencing early signs or more advanced stages of hair loss, there are effective solutions available.
If you are concerned about hair loss, consult with our trichologists who can provide personalised advice and treatment options based on your specific stage of hair loss. Book an appointment today to explore the best hair loss treatments for you and take a significant step towards regaining your hair and confidence. From the initial stages of balding to more advanced alopecia stages, our specialists are equipped to offer the latest in PRP treatment for hair loss and other effective therapies.
Frequently Asked Questions
Yes, it is possible to regrow your hairline depending on the cause of hair loss. Treatments such as minoxidil, finasteride, and certain hair transplant procedures like FUE (Follicular Unit Extraction) can be effective. However, success largely depends on the underlying cause and how early treatment is started.
Hair can regrow in bald spots, especially if the cause is conditions like alopecia areata or if the baldness is not long-standing. Treatments such as corticosteroid injections, PRP (Platelet-Rich Plasma) therapy, or topical immunotherapy can help stimulate regrowth in these areas.